Hemoglobin is a protein inside red blood cells. Hemoglobin carries oxygen from the lungs to all the cells of the body. Like other proteins, hemoglobin can join with sugars, such as glucose. When this happens, it becomes glycated hemoglobin, referred to as A1C or glycohemoglobin (or sometimes as HbA1c). The more glucose there is in the blood, the more hemoglobin will join with it. Once joined, hemoglobin and glucose stay that way for the life of the red blood cell—about 4 months.
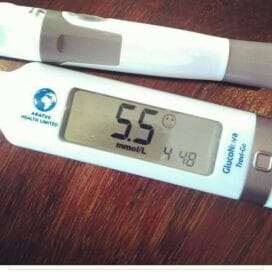
The A1C test measures the amount of glycohemoglobin in your red blood cells. The A1C test is usually done by a lab. A sample of your blood is taken. The blood can be taken at any time of the day. It does not matter what food you last ate. It does not matter what your blood glucose level is at the time of the test.
What the A1C Test Can Do
• Tell you about your average blood glucose level for the past 2 to 3 months. You can then see how your blood glucose control has been. An A1C < 7% is good for most people, while an A1C > 9% is considered very poor control. Some reports will now give the A1C value expressed as a percent together with an average blood glucose value in mg/dl. This is known as your estimated average glucose (eAG).
• Allow you to compare the A1C test results with blood glucose checks you do yourself or tests your doctor has done. If the tests do not agree, you may need to change the way or the times you check your glucose levels at home.
• Help you judge whether your diabetes care plan is working. If your glycohemoglobin indicates that your blood glucose level was high during the past 2–3 months, something in your plan may need to be changed.
• Show you how a change in your plan has affected your diabetes. Perhaps you started to exercise more. An A1C test can confirm the good effects exercise has had on your blood glucose control.