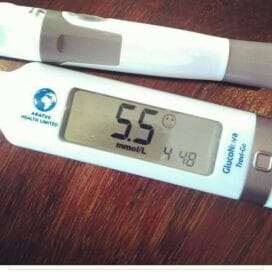
The American Diabetes Association recommends avocado as a healthy source of monounsaturated fats. Avocados are one of the best food sources of oleic fatty acids, with around 13 grams per cup of the fruit.
These omega 9 fats are especially recommended for diabetics as they have been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels without reducing beneficial HDL cholesterol (Monounsaturated Fatty Acids and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease). Cholesterol management is regarded as a high priority for people with diabetes as they have a much greater risk of developing heart disease.
The oleic acid in avocados can also help reduce high triglyceride levels in the blood, another big predictor of cardiovascular disease.
Additionally, adding more monounsaturated fats to their diet is believed to help people with diabetes process glucose and use insulin more effectively. An even richer source of monounsaturated fats and one of the healthiest oils for cooking is avocado oil.
Diabetes and Vitamin C
Vitamin C is important for diabetes in a number of ways. It strengthens the body’s blood vessels, especially the small capillaries that are more at risk of damage for diabetics. It helps with wound healing and can improve our immune system.
Vitamin C also reduces high levels of sorbitol sugar in the blood of diabetes sufferers (Nutraceuticals in Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome). Sorbitol accumulation in the body can result in deteriorating nerve function and damage and is very important for diabetics to keep under control.
Diabetes is a disease that exhibits significant oxidative stress throughout the body. Natural antioxidants like vitamin C can help reduce free radical damage that can lead to heart disease, diabetic neuropathy and many other disorders.
Though #largedoses of supplemental vitamin C have had both #positive and #negative results in scientific studies, researchers have concluded that people with the highest levels of vitamin C circulating in their blood are much less likely to develop type II diabetes.
High blood levels of vitamin C are best achieved by eating vitamin C rich superfoods like avocado. Other good sources of vitamin C include #papaya, #kiwi fruit, #broccoli, #citrus fruit, #strawberries, #bell pepper, and green superfoods like #kale and#parsley.
One final important point to note with diabetes and vitamin C is that high doses may skew the results on a blood test for diabetes or daily blood glucose tests. Given this, it would be best to take vitamin C several hours away from any blood testing.
High Potassium Levels
Avocados
are a great source of the mineral #potassium,
without the relatively high carbohydrates of some other potassium
rich foods like bananas. This makes them an especially good addition
to a diabetic diet.
Potassium is essential for maintaining a
healthy cardiovascular system and normalizing blood pressure, both
highly important for diabetics and those at risk of the disease. Your
pancreas needs potassium rich foods to operate at its best and the
mineral is also heavily involved in insulin function.
Other superfoods high in potassium include #parsley, #coconut, walnuts and pumpkin seeds.
Vitamin E Rich Avocados for Diabetics
Avocados are rich in vitamin E, which is an excellent antioxidant for neutralizing free radicals, particularly in the arteries. Good levels of vitamin E in our diet can help prevent LDL cholesterol from oxidizing, leading to the arterial plaque buildup that can cause heart attacks and strokes.
Vitamin E may also provide extra protection from diabetic nerve damage in type II diabetes. One study showed that defective nerve conduction in diabetic subjects with peripheral neuropathy was improved with vitamin E supplementation (Reversal of defective nerve conduction with vitamin E supplementation in type 2 diabetes).
People living with diabetes would likely benefit from more natural vitamin E in the diet. Vitamin E supplements are often recommended for diabetics but there is concern the most vitamin E formulations are unbalanced, being made of alpha-tocopherol only. Far better results have been reported with a more natural range of tocopherols (especially gamma-tocopherol) and complementary tocotrienols, just as vitamin E occurs across a broad range of foods in nature.
Other Nutrients for Diabetics in Avocados
Along with their monounsaturated fats, vitamin C, potassium and vitamin E, avocados also contain several other nutrients that are especially beneficial for diabetics.
Avocados contain most of the B vitamins, including thiamine, niacin, riboflavin, pyridoxine and folate. Low plasma concentrations of thiamine (B1) have been observed in diabetic patients and this deficiency has been linked to a range of problems associated with diabetes, including both kidney and vascular disease (High prevalence of low plasma thiamine concentration in diabetes linked to a marker of vascular disease).
Avocados are a source of thiamine but, with diabetics needing extra, regularly eating an even richer source like tahini or organic sunflower seeds seems like a good idea.
Riboflavin (B2) deficiency is also often observed in diabetics, particularly children. Riboflavin is needed for cell function and the normal metabolism of carbohydrates, protein and fats. Liver, organic almonds, wheat bran and dried parsley are all good sources.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is another B vitamin that is important in diabetes. Pyridoxine can help to normalize blood glucose levels and a deficiency of this nutrient is associated with higher oxidative stress and metabolic diseases like diabetes. Best food sources include rice bran, raw pistachio nuts, wild salmon and organic sunflower seeds.
The niacin (B3) in avocados can help reduce LDL cholesterol levels and triglycerides. While good levels of folate (B9) may help improve diabetic neuropathy and is needed for a healthy cardiovascular system. Much more on both of these in Eating Avocado for a Healthy Heart.
Along with potassium, magnesium is another important mineral for diabetics to get sufficient amounts of, especially as so many of us are deficient in it. A lack of magnesium is recognized as a risk factor for heart disease, high blood pressure and even developing diabetes in the first place.
Pumpkin seeds and organic brazil nuts are good sources of magnesium to add to your diet. Many people use magnesium supplements, but these are often poorly absorbed in our digestive system.
Finally, avocados are also a very good source of dietary fiber to help stabilize blood sugar levels.